Business Areas
Hazardous Cargoes
 > Business Areas > Hazardous Cargoes
> Business Areas > Hazardous Cargoes
DANGEROUS GOODS SERVICE
Service Overview
The hazard levels of the cargoes are confirmed based on the mode of transportation and the local laws and
regulations, and efficient work approaches are provided to our clients.
UN certified vessels, packaging, and labels are provided for dangerous goods in accordance with the IMDG
codes and DGR.
Safe storage of dangerous goods and prompt customs clearance services for the government agencies,
importation, and exportation customs authorities.
What are Dangerous Goods?
Dangerous goods are the materials or products which have the risks of explosion, ignition, poisoning, corrosion, radio activity,
suffocation, fire, infestation, polymerization, frostbiting, dust explosion or reactions due to their physical, chemical properties of
the materials, contacts between the materials and one or more other substances, or under other special circumstances, resulting
in risks to the health, safety, properties, or environments. In short, the dangerous goods are those registered with the IMDG Code
as Dangerous Goods.
MSDS
MSDS means the Material Safety Data Sheets, which specifies the risks and hazards, first-aid procedure, and handling methods, in order to ensure safe handling of chemicals.
UN no. and PSN.
The Dangerous Goods registered with IMDG Code are endowed with the proper shipping names and the unique United Nations
Number for their identification, so that they can identified easily in case of an emergency. The UN Number is a unique number assigned
to a dangerous good by the Dangerous Goods Transportation Export Committee. Each of the dangerous goods registered under IMDG
Code is assigned with a corresponding UN number.
IMDG
IMDG, or International Maritime Dangerous Goods Code, was introduced in 1965, in response to the needs to transport dangerous
goods safely through a standardized regulation system based on their mode of transportation. IMDG Code assigned the dangerous goods with grades of dangers (Grade 1 through 9) in accordance with the level of risks the material or product has, in order to increase the
efficiency in managing them.
Classification of Dangerous Goods in IMDG
| Hazard Label | Class | Name | Description / Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Grade 1 | Fire powder | TNT, Dynamite or Torpedoes | |
| Grade 2 | High-pressure gas | Butane, Hydrogen, Propane, Lighters | |
| Grade 3 | Inflammable liquids | Certain Paints, Varnishes, Alcohols | |
| Grade 4 | Combustible materials | Matches, Sulphur, Celluloid | |
| Grade 5 | Oxidizing materials | Ammonium nitrate fertilizer, Calcium | |
| Grade 6 | Toxic materials | Arsenic, Nicotine, Cyanide | |
| Grade 7 | Radioactive materials | Radionuclides or Isotopes | |
| Grade 8 | Corrosive materials | Battery acids, Mereury, sodium hydroxide | |
| Grade 9 | Harmful substances | Battery acids, Mereury, sodium hydroxide |
Transportation of Dangerous Goods in accordance with the UN Standard
There have been active efforts to prove the risks in an objective manner. However, the dangerous goods are defined rather by the
regulations of UN than the specific chemical composition of the material. For this reason, it is only possible to define a material
as a dangerous good when one clearly understands the regulations of the United Nations and the classifications of the dangerous
goods in accordance with these rules. In the end, this can ensure safe transportation of the goods, in compliance with the regulations.
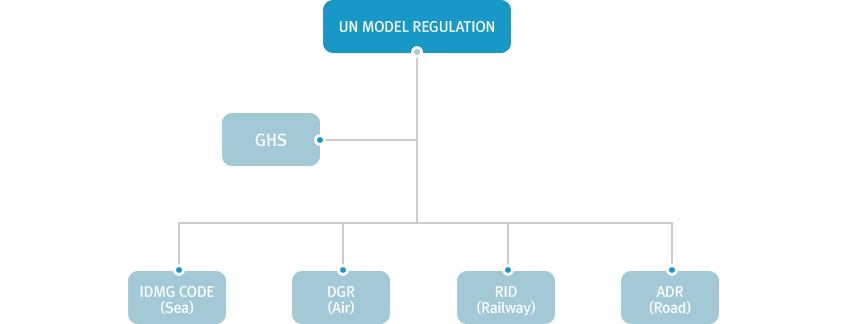
As such, there are four international organizations which oversee the transportation of Dangerous Goods. Also, the compulsory
regulations, such as fining, rework orders, or SHIP BADK, are in accordance with the policies of each country, which may differ among
the mselves.
| UN Recommendation | UN Recommendation on the transport of dangerous goods |
| ECOSOC | United Nations Economic and Social Council |
| IMDG | Intemational Maritime Dangerous Goods Code |
| AND | European Agreement for the Intemational Carriage of Dangerous Goods by inland Water way |
| TI | Technical Instructions for the Sate Transport of Dangerous Goods by Air |
| ADR | European Agreement conceming the Intemational Carriage of Dangerous Goods by Road |
| RID | Regulations conceming the Intemational Carriage of Dangerous Goods by Rail |



